By default you can’t install TeamSpeak Server on a Raspberry Pi. That’s because TeamSpeak is made for x86 processors and Raspberry Pi only comes with ARM processors.
To install TeamSpeak Server on a Raspberry Pi you need to install an emulator. In other words you have to make your ARM processor understand packages made for x86 processors.
In this guide I will use the Box86 emulator.
Setup the Raspberry Pi for Box86
1: First we have to update the system with these two commands:
sudo apt updatesudo apt upgrade2: Now we need to install all the necessary packages to compile Box86:
sudo apt install git build-essential cmake3: Now clone the latest GitHub version:
git clone https://github.com/ptitSeb/box86If you have a 64-bit operating system follow these steps. If your operating system is 32-bit; don’t!
(4): Add the 32-bit architecture to the package manager:
sudo dpkg --add-architecture armhf(5): Update the package manager:
sudo apt update(6): Install the needed packages:
sudo apt install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf libc6:armhf libncurses5:armhf libstdc++6:armhfCompile Box86
1: Change into the driectory where we downloaded Box86 to:
cd ~/box862: Make a new directory called ‘Build’ and change into it:
mkdir buildcd build3: Now choose the right command for your Raspberry Pi and OS:
For Raspberry Pi 4, 32-bit:
cmake .. -DRPI4=1 -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelWithDebInfoFor Raspberry Pi 4, 64-bit:
cmake .. -DRPI4ARM64=1 -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelWithDebInfoFor Raspberry Pi 3:
cmake .. -DRPI3=1 -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelWithDebInfoFor Raspberry Pi 2:
cmake .. -DRPI2=1 -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelWithDebInfo4: Now we have to compile Box86. This can take a very long time!
make -j$(nproc)5: Once finished we have to install the compiled Box86 emulator:
sudo make install6: Now we have to restart the systemd-binfmt service:
sudo systemctl restart systemd-binfmt7: All we have to do now is reboot:
sudo rebootSetup and install TeamSpeak Server
1: Start by updating:
sudo apt updatesudo apt upgrade2: Install ‘jq’:
sudo apt install jq3: Create user ‘teamspeak’:
sudo adduser teamspeakJust hit Enter and skip through and confirm with Y(es).
4: Switch user to ‘teamspeak’:
sudo su - teamspeak5: Download the latest Linux x86 version of TeamSpeak Server:
wget $(curl -Ls 'https://www.teamspeak.com/versions/server.json' | jq -r '.linux.x86.mirrors | values[]')6: Extract the downloaded package:
tar xvf teamspeak3-server_linux_x86-*7: Remove the package from where we extracted:
rm teamspeak3-server_linux_x86-*8: Change into the TeamSpeak Server directory:
cd teamspeak3-server_linux_x869: If you agree to the TeamSpeak license agreement:
touch .ts3server_license_accepted10: Start the server for the first time:
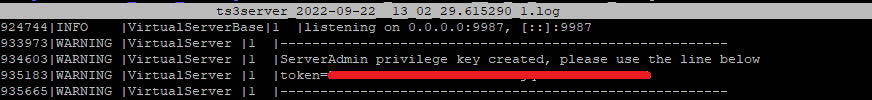
./ts3server11: On the first startup it will post an admin token (privilege key) that you will need later in the TeamSpeak Client.
12: When you have copied the token you can shutdown the server for now by pressing Ctrl+C
13: Exit the ‘teamspeak’ user:
exitConfigure the server to start at boot/reboot
1: Create a service file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/teamspeak3.service2: Copy-paste the following into the service file:
[Unit]3: Save and exit the file by pressing Ctrl+X, then Y and then Enter.
4: Reload systemctl daemon:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload5: Enable the TeamSpeak Server service:
sudo systemctl enable teamspeak36: Start the TeamSpeak Server:
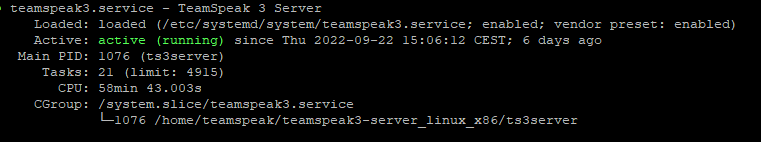
sudo systemctl start teamspeak37: Check the status of the TeamSpeak Server:
sudo systemctl status teamspeak38: Exit by pressing Ctrl+C
Conclusion
Congratulations! If you have followed every step of this tutorial you should now have a working TeamSpeak3 Server running on your Raspberry Pi.
If you have any questions or comments please post them below.
Versions
1.0 28-09-2022 First post